



1a. Describe three types of equilibria that are found on a Eh-pH (Pourbaix) diagram. Include how and why each differs from the others in terms of their response to changes in pH and electrode potential. (5 points each)
1b. Label the following reactions as to their type (i, ii, or iii above): (1 point each)
|
CuO + 2 H+ = Cu2+ + H2O |
iii vertical |
|
Cu = Cu2+ + 2 e- |
i horizontal |
|
Cu2O + 2 H+ = 2 Cu2+ + H2O + 2 e- |
ii sloped |
|
H+ + e- = 1/2 H2 |
ii sloped |
|
Cu(OH)2 + 2H+ = Cu2+ + 2 H2O |
iii vertical |
|
4 OH- = 2 H2O + O2 + 4 e- |
ii sloped |
1c.Calculate the reversible potential for the above H2 reaction (H+ + e = 1/2 H2) in a pH = 4 solution
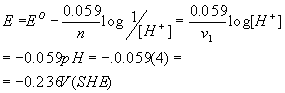
2a. Draw an electrical circuit for polarization of a sample in the cathodic (reduction) direction using a battery, and other circuit elements. Label all circuit elements, show the current flow direction, show the anion and cation flow directions in the electrolyte, show the polarity of one of the battery terminals, i.e., (+) if the battery attracts electrons and (-) if the battery repels electrons, and state which meter outputs are the axes of the polarization curve.
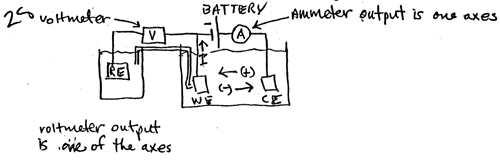 |
Label I 2 Battery polarity 2 WE 1 Flowdir 2 CE 1 RE 1 Meters 2 Axes 2 |
2b. What are the two circumstances that determine the optimum positioning of the Luggin capillary tip with respect to the W.E. surface? (5 points each)
In this regard define parameters in the relation 1>2D and explain how to modify them in order to minimize the IR component of the measurement E voltage while remaining consistent with (i) and (ii).
L=distance between the tip and the W. E. surface.
D=outside diameter of the Luggin capillary tip.
Decrease D so that L decreases. The tip can now be placed closer to the W. E. without affect the reaction rate (i above) and so the measured voltage is closer to the true E (iii above).
The valency is higher in the product species for an oxidation reaction, and the valency is lower in product species of a reduction reaction.
Formation/application of an insulator coating, an inert protective coating, a protective noble metal coating, etc. are all answers.
4a. Would a piece of copper corrode in a 25 C acid solution (pH0, [Cu2+] = 10-6 M) exposed to air? (2 points)
Support your answer with a calculation of the free energy change. The relevant equilibria are some of the following reactions:
| Cu2+ + 2e- = Cu Cu2+ + e- = Cu+ Cu(OH)2 + 2e- = Cu + 2 OH- H+ + e- = 1/2 H2 O2 + 4H+ + 4e- = 2H2O O2 + 2H2O + 4e- = 4OH- |
Eo = 0.34 V Eo = 0.16 V Eo = -0.224 V Eo = 0 V Eo = 1.229 V Eo = 0.401 V |
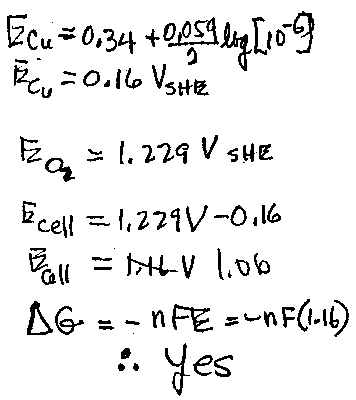
|
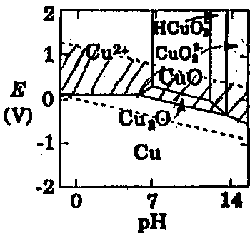
4b. Crosshatch the E- pH area on the accompanying diagram where Cu will corrode. (5 points)
Last up-date: 23 Aug 1999.